介绍一种事物的说明文500字,介绍一种事物的说明文400字
2023-10-11 22:00:21
初中英语教案设计范例 初中英语教案设计心得与反思
初中英语教案设计范例。本书以“学生为本”为出发点,以“提高学生的综合素质”为目标,以“培养学生的创新精神和实践能力”为核心,力求做到“内容新颖、、结构合理、语言通俗、深入浅出”。
这节课应该既能够让学生的学习有意义,也能够让教师在扎实、充实、平实、真实的授课过程中真正享受到,“教学作为一个创造过程的全部欢乐和智慧的体验”。以下是我为您整理的初中英语优秀教案范文,供您参考,更多详细内容请点击教案栏目查看。
篇一:《How do you get to school》
一、对本节课的定位
我认为在“新课程标准”和“新基础教育”的理念的指导下,这节课应该既能够让学生的学习有意义,也能够让教师在扎实、充实、平实、真实的授课过程中真正享受到,“教学作为一个创造过程的全部欢乐和智慧的体验”。同时,本单元是以话“交通”题材为教学主要内容的新目标(Go for it)教材典型设计,借助本单元可以给学生在学习 *** 上以很好的指导,并可以在小空间内进行大规模的扎实、有效的训练。
二、任务目标的确定
本单元的教学任务是在“交通(transportation)”这一话题下,让学生学会谈论“交通”(包括不同的交通方式,到某地的距离以及以某种交通方式到某地所花费的时间等),学习一些文化常识,掌握一定的学习 *** ,并在大量的、有效的训练中提高学生的听说读写等基本能力。
三、教学环节的设计思路
本着整体划一,循序渐进,高效有序,并在教学中能不断地深化教学的设计思路来安排本节的每一个环节。
(一)整体划一
在本节课中,对于“整齐划一”可以从两点来说明: 首先,本人一直认为作为语言教学,听说读写等能力的训练应该是一个整体,不可分割开来的,因此在教学设计中可以说一个话题,一个训练都蕴含着各种能力的培养;其次,在教学中每一节课都是独立的,但在我的教学设计中每一节课不仅可以独立,更重视它在单元教学整体中的地位与作用。与每一节课内衔接一样,单元教学的整体衔接也很重要。
(二)循序渐进,高效有序
本节课从简单的对“How do you get to school in the morning?”的询问入手,引入对重要课文Section A 3a 的复习。通过学生复述这段文字,重点巩固由“How, How long, How far”引导的谈论交通话题的重要句型,并提炼相关的信息形成新的对话,为下一环节作铺垫。即课文Section A 3b 的训练,通过第一、二人称来谈论交通话题的训练,拓展到以第三人称来谈论他人的交通话题,进而让课文Section B 2a, 2b, 2c 的学习水到渠成。然后完成对本节课学习的测试,进行归纳总结本节课的要点。最后,作业一中让学生来完成交通方式的图片收集,是对本节内容的进一步深化;作业二中要求学生做一个调查,并形成调查报告,实际上和测试二一起构成了对Section B 3a 的有效预习。
总之,本课从课本入手,用课本内容引出一系列的活动,最终又导向课本,环节紧扣,层次清晰。
四、独特的创意
本节课的设计中,具有独特创意的地方,可以从以下几个方面来说:
第一、独特的环节设计
首先面向全体学生进行简单的复习,目的在于巩固几个基本句型。然后把课本中阅读的短文用复述和听力的方式引入,别出心裁。其主要目的在于营造较轻松的语言环境,缓解部分学生对于说写等输出环节的畏惧心理。接下来,从大量的听说引入读写,给学生铺垫知识的过程。既练习口头表达,又巩固了读的成效。教学步骤中每一步都将成为下一教学步骤的铺垫,在每一步骤中,教师设计具体任务,让学生参与到课堂互动中,并完成具体的任务。整个课堂设计由浅入深,循序渐进,难度过渡非常自然。
第二、独特的课程深化
全面展开训练,重点集中突破,中考真题帮辅,课结影响未尽。首先,在常规的训练之后,又用中考真题来重点训练和巩固所学,不但给学生对本节课的理解有更深一步的认识机会,更为学生的长远学习打下了坚实的伏笔。其次,在对交通的表达方式上的深化,采用了系统归纳,并用同意表达的形式进行训练,有层次,有实效。
第三、独特的思维能力训练
着重思维能力的训练,围绕话题进行多方面的扩展性的练习,并充分地利用 Listening 和Speaking,引发学生积极思维,以Groupwork和Pairwork等多种形式讨论和操练。最终达到让学生熟练谈论“交通”这一说话能力的目标。并在作业中以预习形式对这一目标进行了延伸。
五、掌控好借来的学生
由于是借班上课,学生又是活动的主体,课堂上大部分的时间交给学生,教师的引导是关键。
篇二:《How often do you exercise》
Unit 1 How often do you exercise?
Ⅰ.Analyis of teaching material
1.The topic of this unit is about free time actmties。Suchtopicisrelated to students’daily life. So it is helpful toraise learning interest of students. If students can learn this unit well,it will be helpful to make students learn the the rest of this book.
2 .Teaching Aims and Demands
(1) Knowledge Obj ect
In this unit students learn to talk about how often they do things.
(2)Ability Objects
To improve students’ability of listening,speaking,reading and writing.
(3)Moral Objects
To help students form a good eating habit.
To do exercise every day and keep fit.
3 .Teaching Key Point
To master the key vocabularyand the target language presented in this unit.
4 .Teaching Difficult Point
To train students how to use the key vocabulary and the target language by reading and writing.
5 .Studying Ways
Teach students how to use context.
Teach students how to do a survey.
Ⅱ.Language Function
Talk about how often you do things.
Ⅲ.Target Language
What do you usually do on weekends?
I sometimes go to the beach..
How often do you eat vegetables?
Every day.
Most of the students do homework every day.
Ⅳ.Structure
Wh-questions
What do…?
How often…?
Adverbs of frequency
All/most/some/none
V .Vocabulary
always,usually,often,sometimeshardly,ever,never, exercising,shopping,skateboarding once,twice,three times a week,month, every day, milk,junk,food, drink
Ⅵ.Recycling
reading,watching TV,go to the movies, fruit,vegetables
Ⅶ.Learning strategies
Using context.
Transforming information.
Ⅷ.Teaching times
Six periods
Period One
Teaching Aims:
1. Learn to talk about how often do you do things
2. To learn the words of the adverbs of frequency.
Teaching Difficulties:
1.words: exercise, skateboard, hardly, ever, shop, once, twice, time, surf, internet, program.
2.phrases:how often, on weekends, go to the movies, exercise, go skateboarding, always , usually , often , never , hardly ever , sometimes .
3.Sentence patterns: What does she /he do on weekends ? She often goes to the movies .How often do you shop ? Once a week / Twice a week ••• .
Teaching Aids: Tape recorder;Multi-Media.
Teaching Procedures:
Step 1 :Greeting.
1. Teacher: Summer vacation is over. I think you had a wonderful vacation, am I right? Did you enjoy your summer vacation? Could you please tell us what you did in your summer vacation?
2. Encourage students to share their holidays with the whole class.
Step 2 :Leading – in
Teacher: Oh, you had a happy and colorful vacation. Today we will talk about more activities on weekends. First, let’s think about what we can do on weekends. (Ask some questions and let students think it over).
Teacher: I often sing on weekends, what do you usually do on weekends?
S1: I often take piano lessons.
Teacher: What does she usually do on weekends? (Ask another student)
S2: She often takes piano lessons.
Teacher: What about you? (Ask S2)
S2: I often play basketball
Teacher: What does he usually do on weekends? (Ask another student)
S3: He often plays basketball.
(Ask more students in the same way)
Step 3:1a Look at the screen. Make a list of the different weekend activities.
First let students list different activities, then
Teacher: Now work in pairs, ask and answer
---What does he/she do on weekends?
--- She goes shopping. / She reads books. / He exercises. / He watches TV. / She goes skateboarding.
Step 4:1b Listen and write the letters from the picture above on the lines below.
Get students to focus on the six adverbs in activity 1b and help students to understand:
Always-100% usually- 90% often-80% sometimes-50% hardly ever-10% never-0%
Step 5:Lead-in:
Teacher: I always read English books on weekends.
I usually exercise on weekends.
I often go to visit my grandparents.
I sometimes go shopping on weekends.
I hardly ever play computer games on weekends.
I never play cards on weekends.
What does your English teacher do on weekends?
(Help students to say)
Students: Our English teacher always reads English books on weekends. She usually exercises on weekends…..
Teacher: I exercise every day. I go shopping once a week. I watch TV twice a week. I go dancing three times a month…
How often does your English teacher exercise/ go shopping / watch TV / go dancing?
Students: Our English teacher exercises every day….
Step 6: Listening (2a and 2b)
Teacher: My friend Cheng is talking about something about his different activities, let’s listen and number the activities you hear.
Teacher: Listen again. How often does Cheng do the activities above?
(Help students to finish 2a and 2b)
Step 7:.Do a survey:
Activities How often
Take a shower
Wash your hair
Exercise
Clean your room
Ask and answer: How often do you take a shower?
How often does he / she take a shower?
Let Ss ask and answer in pairs, using always, usually, often, sometimes, hardly ever or never.
篇三:《Where’s your pen pal from》
教学目标分析
1、语言目标
a. 重点词汇:
Countries: Canada, China, France, Japan, the United States, Singapore, Australia, The United Kingdom, Paris.
Cities: Sydney, New York, Toronto, Toyo, London
Languages: English, French, Japanese, Chinese.
b. 重点句型: -Where…from? -She’s/He’s from…
-Where does…live? -She/He lives in …
-What language does she /he speak? -She/He speaks ….
2、能力目标
a. 培养学生在文段中寻找信息的能力;
b. 学会用英文给笔友写回信,简单介绍个人情况;
c. 通过有效地小组合作,培养学生合作能力及团队精神。
d. 在连惯的听说读写活动中,训练学生的逻辑思维,快速反应能力和实践能力 , 使学生能熟练运用新句型来谈论年龄和日期。
3、交际目标
通过学习本单元的内容,使学生学会用各种方式与世界各国朋友交流。
4、德育目标
了解世界,了解不同地区的人文风俗;学会理解和尊重异国文化。
三、单元重难点分析
重点: 1. 谈论国籍、民族及其语言。
2. 询问并回答人们的住处。
难点: 1. 含from的where引导的特殊疑问句及其回答
2. 含live的where引导的特殊疑问句及其回答
四、课时结构
为了能较好地实现既定的教学目标,结合本单元教学内容和学生的学习规律,将本单元授课时定为四课时。
Period 1 Section A 1a—2d
Period 2 Section A 3a—Section B2c
Period 3 Section B 3a---3c
Period 4 Summing up Section A and B and the grammar.
五、教学过程设计
The First Period
Teaching aims:
1.Learn to express the main countries and cities.
2.Know something about the countries.
3.Master where- sentence structure.
Key points:
1. Words: pen pal, Australia, Japan, Canada, France, the United states, Singapore, the United Kingdom, country, Sydney, New York, Paris, Toronto, Tokyo world
2.Sentences: -Where is your pen pal from? -He’s from Australia.
-Where does he live? - He lives in Paris
-Where is John’s pen pal from ?
Teaching aids:
Some cards with cities and countries.
Teaching procedures:
Step 1.Lead—in (1a&2a)
First greet the students. Then teacher begins the topic with the Spring Festival. Do you have a nice Spring Festival? Do you go to many places? I do. Then use the fresh pictures through computer to teach the students names of countries, cities. Divide the students into groups, then show the flags and pictures, let them guess the names of countries and cites. At last finish 2a on page2. 通过这个环节,教师完成本单元的新单词的导入,通过提供给学生每个国家的地图,让学生猜出国家名称及相应的城市,学生能有意识的记忆国家及城市的名称,并为整节课任务的完成奠定最基本的词汇基础。在看图片时学生能够做到精神集中,并能激发学生的学习兴趣。
Step2.Practice(1c&2d)
①Teacher says: I goes to many places during the Spring Festival, so I have many pen pals from different countries. One of my pen pals is Sandy. She is from the UK. She lives in London. Ask the students: Do you have a pen pal? Some say yes, some say no. Then go on with “Where is she/he from?” and “Where does she/he live? Ask some students to stand up and practice with teacher.
②With these sentence structures, ask students to practice them in pairs.
③Make a Survey to understand your clas *** ates better.
上面这些句型的操练都是为了最后一个任务作铺垫。操练的过程中可以及时纠正学生的错误。然后让学生填写调查表,了解全班同学的笔友分别来自哪个国家以及居住在哪个城市,同时让学生认识和了解一些国家和城市相关地理文化知识,拓展学生的视野, 激发他们的兴趣。在完成任务的过程中运用where…from和where…live引导的特殊疑问句, 综合运用目标语言, 询问并回答人们的国籍和住处。
Step3.Listening comprehension(1b,2b&2c)
After practice, do a lot of listening exercises. Finish 1b on page 1 and 2b & 2c on page 2.在口头练习的基础上,在他们熟练掌握本课时句型以后再做这些听力应该是不难了,这样可以增加他们学习英语的信心。并且这些听力材料的设计也是层层递进,由易到难,充分考虑到了学生的层次,起到了很好的巩固作用。
《新课标》倡导英语课堂要以主题意义统揽教学内容和教学活动,即英语教学要在主题意义引领下开展学习理解、应用实践、迁移创新等英语学习活动。
“基于主题意义的单元整体教学”的提出为解决教学设计缺乏纲领性统领,内容碎片化、过程表面化、评价形式化等问题提供了思路和方案。
目前,我们一线教师已广泛接受基于主题意义的单元整体教学理念,但在实际操作过程中却存在一些问题。
一
单元主题意义界定不明确
教师对主题意义的界定不明确,且未能将教学内容、教学活动与主题意义相关联,对主题意义的探究未能发挥统领作用。
教材的每一个单元在编写上围绕特定的主题,但主题内容松散地分布于单元的不同部分,且联系并不十分紧密。
因此,教师要将零散的内容串成一个逻辑性较强的整体,就需要充分挖掘并分析教材,包括对单元标题、单元语篇、文体、词语等文字材料以及文中插图、表格等非文字材料深入分析,进行拆分和整合,从而确定单元主题意义。
案例一:
人教版九年级Unit 9 I Like Music that I Can Dance to.该单元共有三个版块。
Section A 1a-2d为第一版块,主要介绍喜欢的音乐或电影类型;
Section A 3a-4c 为第二版块,主要介绍不同情绪下适合观看的电影类型;
Section B 为第三版块,主要是让学生运用所学目标语言谈论其喜欢的音乐和电影类型或其他喜好,并进行评价。
三个版块都围绕同一单元主题---健康的休闲娱乐方式展开。因此,通过对单元内容进行分析整合,便可以清晰明确地界定出本单元的主题意义。
二
主题意义探究浅层化
教师在对主题意义进行探究时,常停留在语篇的表层内容上,且教学的焦点始终围绕在对教材文本的理解上,致使探究范围狭窄,无法有效地拓宽学生的思维。
教师在教学过程中要正确认识文本解读的内涵。文本解读不仅仅是对文本中所涉及的语言知识的解读,还包括文本语境、主题脉络、文本体裁、篇章模式、文本结构、写作手法、
这就需要教师根据文本特点,设计出多维度、多层次的文本解读活动,从而拓展学生思维的深度和广度,培养学生独立思考、分析问题和解决问题的能力,为运用所学知识进行迁移和创新奠定语言和思维基础,并以此获得新知识,建构新概念。
案例二:
人教版九年级Unit 5 What Are the Things Made of?
该单元主题为Things in China. 语篇主要包含Chinese tea, Chinese products, Chinese art forms三个版块。
其中,在版块一的文本An Accidental Invention中,许多教师在课堂授课过程中已经有了深挖文本的意识,然而却停留于对表层的文本语言知识进行分析和讲解,忽视了对文本背后
语篇An Accidental Invention 的文本结构清晰,逻辑性强。文本共分为三段。
文本第一段主要谈论the invention of tea。
以此引发学生思考,并从第一段中找出相关佐证,然后用自己的语言进行阐释。这样可以很好地培养学生发现问题、分析问题和解决问题的能力。
文本第二段强调the production of tea。教师可引导学生在读中对文本内容进行提炼和概括,培养学生的高阶思维;如要求学生在读中环节完成下表:
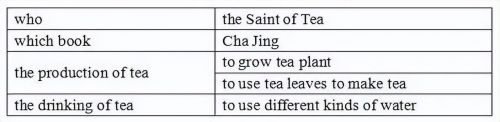
文本第三段强调了the spread of tea。通过阅读第三段不难发现
具体活动设计如下:
Activity 1.
Please discuss with your group members the following questions:
Q1.What’s the author’s writing intention?
Q2.How do you know that?
Please circle the words that can best show the author’s writing intentions.
(设计意图:此活动可以激发学生去讨论并思考
Activity 2.
Please underline the sentences which show the objectivity of the author’s statements.
(设计意图:此活动可以激发学生体会
三
主题意义探究的主体错位
英语学习的过程应是学生主动建构的过程。然而,部分教师在教学过程中常将自己对主题意义的理解灌输给学生,却缺乏对主题意义进行探究活动的指导。
因此,教师可根据学生的认知特点和具体学情,创设与主题相关的情境,引出并激活学生的学习兴趣及过往经验,提高学生的课堂参与度。
在这一过程中,学生以主题意义探究为目的,以语篇为载体,以活动为阶梯,在与文本互动,与
案例三:
人教版九年级Unit 13 We’re Trying to Save the Earth.该单元主题为环境保护。
我区是“紧固件之乡”,在取得不俗的经济效益的同时,环境污染也相对较重。
因此,为使学生能够将文本内容与自己的生活经验相联系,教师可以创设以下主题语境:在引导学生从语篇中感知单元主题的基础上,组织学生对环境现状进行调查,并提出解决办法:
We know it is important to protect the environment.
Please do a survey after class and try to find out:
1. the situation of the environment in our district.
2. the reasons that cause such an environment.
3. use the knowledge you have learned to solve the problems you find.
4. make a poster to call on people to protect the environment.
通过创设以上主题语境,学生可以积极、主动地投入其中,利用现实生活的经验去思考、发现问题、分析问题和解决问题,帮助学生主动建构知识,拓宽并升华单元主题,发展合作沟通和语言表达等多种能力,实现在“做”中活化知识,在“做”中培养思维,在“做”中形成良好的品格,从而学以致用。
结语:
综上,基于主题意义的单元整体教学虽已获得了广泛的认同,然而在教学过程中,我们不免出现上述诸多问题。
但只要我们能做到明确界定单元主题意义;深入且多维度地解读文本;创设主题语境,设计主题学习活动,引导学生积极思考,我们便在培养学生的英语学科素养上又前进了一步。
觉得文章有帮助,点个赞鼓励一下吧!
(3) Do the people under the same star sign share similar characteristics?
I’m having a class.My mother is working.
Knowledge objectives:
2023-10-11 22:00:21
2023-10-11 21:58:06
2023-10-11 21:55:51
2023-10-11 21:53:35
2023-10-11 21:51:20
2023-10-11 21:49:05
2023-10-11 21:46:50
2023-10-11 21:44:35
2023-10-11 15:22:57
2023-10-11 15:20:42
2023-10-11 15:18:27
2023-10-11 15:16:12
2023-10-11 15:13:56
2023-10-11 15:11:41
2023-10-11 15:09:26
2023-10-11 15:07:11
2023-10-11 15:04:56
2023-10-11 15:02:41
2023-10-10 22:06:06
2023-10-10 22:03:51